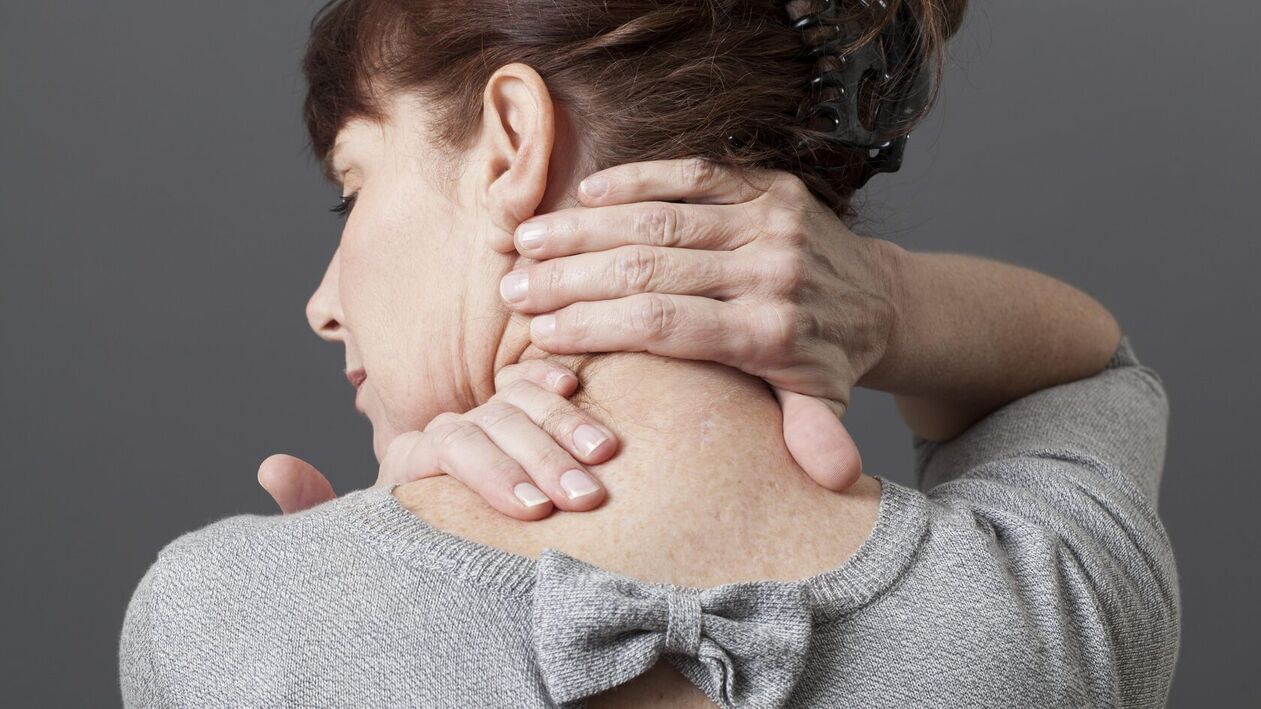
Chondrolysis is an outdated term commonly used in some countries to refer to degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs, facet joints, and vertebral bodies. In the cervical spine, these changes are common due to its mobility and cause neck pain in both men and women. Sometimes the degenerative disease is complicated by intervertebral hernias pressing on the spinal roots, which can lead to muscle weakness and skin numbness in the upper limbs. We will talk about the symptoms and treatment of cervical spondylosis in the article.
Cause of pain
The cervical spine is very mobile. It consists of seven vertebrae, the intervertebral discs located between them, and ligaments. With osteoarthritis, the intervertebral discs become thinner and deformed, their elasticity and shock absorption decrease. Gradually, the inner part of the disc, the nucleus pulposus, protrudes through microscopic lesions in the outer part, called the annulus fibrosus. This is how protrusions and hernias form between the vertebrae, stimulating the pain receptors of the ligaments along the back surface of the spine, causing pain. When the spinal roots are compressed, pain can spread to the upper limbs and neurological symptoms may appear: decreased sensitivity of the skin of the arm, muscle weakness there, etc. v. As a protective reaction to any injury and damage, bone growths - osteoporosis - can appear along the edges of the body and on the vertebral arches.
Cervical spondylosis often develops as a result of aging, but some risk factors aggravate and accelerate the process of spinal degeneration. Among them:
- Genetic predisposition.The presence of osteonecrosis in relatives, especially at a young age, increases the risk of early onset and complications.
- No physical activity.With a sedentary lifestyle, the nutrition of the intervertebral discs is disrupted. They have no blood vessels and receive nutrients by diffusion from the vertebral body. These processes occur actively during physical activity.
- Injury.Spinal injuries accelerate the development of degenerative changes in the spine.
- Uneven load on the spine.Possible situations: improper exercise, wrong posture, load mainly on one side of the body or one limb, tilted head position for a long time, for example, when reading from the phone.
- Metabolic disorder.The condition of the vertebrae is affected by the presence of endocrine diseases, especially diabetes, which make tissue nourishment difficult.
Symptom
The main symptom of cervical spondylosis is pain. Its location depends on the nature of the lesion. When irritated by a bulging disc or bone spurs of sensitive ligaments, you will feel pain in your neck and associated reflex muscle contractions. If the hernia compresses a spinal nerve, pain may radiate down the arm.
Most often, pain is noted in the neck and back of the head, occurring or intensifying with sudden head movements, prolonged static stress, or being in an uncomfortable position, such as after sleep.
Other signs of cervical spine degeneration:
- Neck movement is limited, pain when turning the head.
- Neck muscle spasms.
- Decreased tone and strength of the muscles of the upper limbs, typical of compression due to spinal root herniation.
- Reduced skin sensitivity of the upper limbs.
- When the vertebral artery herniation is compressed, symptoms of vertebrobasilar insufficiency will appear, developing strongly when turning or tilting the head: dizziness, nausea, tinnitus, fainting, short-term memory loss, Unsteady walking, impaired vision, hearing and speech, severe muscle weakness in the limbs.
Diagnose
When experiencing pain and discomfort in the neck area, patients should consult a neurologist or vertebrologist. Sometimes it is necessary to consult other specialists: an orthopedic traumatologist if there is a history of trauma.
A neurologist conducts an examination and clarifies complaints and medical history. Cervical spondylosis can present as dozens of diseases, so additional testing is often necessary to determine the cause of pain and make a clinical diagnosis.
A neck pain diagnostic plan may include the following tests:
- Laboratory tests (general blood count, biochemical blood tests, urine tests, others - as indicated).
- X-ray of the cervical spine to detect fractures and other injuries.
- CT scan of the cervical spine to identify injuries, cancer, and other changes in the vertebrae.
- MRI of the cervical spine to evaluate the condition of the spinal cord, nerve roots, and visualize protrusions and hernias.
- Neuroelectromyography to determine impulse conduction along the spinal roots.
During the differential diagnosis, other tests are also prescribed at the discretion of the specialist.
When can treatment be performed without surgery?
For cervical spondylosis, conservative treatment is performed if there are no progressive neurological manifestations: muscle weakness and numbness in the limbs. They occur when spinal roots, arteries, and spinal cord are compressed.
The neurologist determines how to treat cervical osteoarthritis after examining and receiving the results of the examination. Most patients receive effective conservative treatment with stable long-term remission. Modern techniques are also used effectively to prevent the progression of osteonecrosis and its manifestations.
Conservative treatment methods
For cervical spondylosis, therapy begins with conservative methods. Its goals: relieve pain, eliminate muscle spasms, improve metabolic processes in nerve tissue and microcirculation.
Drug treatment is performed to relieve pain and muscle spasms. To do this, the neurologist prescribes nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and muscle relaxants. If the pain persists for more than 12 weeks, i. e. becomes chronic, anticonvulsants and antidepressants with long-lasting pain relief may be recommended.
In addition to drug treatment, modern and effective techniques are also used:
- Acupuncture.The neurologist uses special sterile needles to stimulate biologically active points. This alleviates the condition: reduces pain, relaxes muscles.
- Plasma therapy.With the local use of plasma enriched with the patient's own platelets, the regeneration of damaged tissues is stimulated. Recovery time after surgery, illness and injury is reduced.
- High strength magnet.Electromagnetic fields stimulate and accelerate the regeneration of damaged tissues. Reduce pain and reduce swelling.
- Laser physical therapy.This method has anti-inflammatory, anti-edema and pain-relieving effects. It allows you to reduce the size of the hernial protrusion. It is used as a basic method as part of the treatment of intervertebral hernia by resorption.
- Physical therapy.Classes are aimed at strengthening muscles, increasing the flexibility of the spine, restoring range of motion in the spinal joints and developing correct posture. Exercises are individually selected by specialists for patients after acute pain has subsided.
- Kinesio recording.Combined with physical therapy. Before class, the doctor applies adhesive tape to the neck area in a certain direction to relax the muscles and affect pain receptors. As a result, the pain gradually decreases. With regular use, spinal mobility is restored and muscle tone is normalized.
- Medical massage.The specialist reduces muscle spasms by acting on receptors in the skin, muscles and fascia. Rapid and permanent pain relief and improved mobility of the vertebrae.
Therapy is selected individually depending on the cause of neck and back pain and accompanying symptoms.
Forecast
With timely diagnosis and treatment, the outcome is favorable. If complications of osteoarthritis appear in the form of intervertebral herniation with various neurological symptoms, surgical treatment may be required. After that, recovery can last for many years. Without treatment, there is a high risk of permanent disability. Comorbidities and advanced age worsen prognosis.
Patients are often interested in the question of how to get rid of cervical spondylosis forever. Unfortunately, it cannot be completely cured. Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine are an inevitable natural aging process of the body. But you can slow their progression and avoid complications.
Prevent
There are no specific prevention measures for osteonecrosis.
Recommendations to improve overall health:
- Maintain optimal body weight.
- Maintain an active lifestyle.
- Sleep on an orthopedic mattress and pillow.
- Regular moderate physical activity - half an hour of walking, warming the neck and back every day is enough.
- Ergonomics of the workplace. The desk and chair should be suitable for your height, the computer screen should be at eye level or slightly higher.
These measures will maintain the health of the musculoskeletal system by reducing the rate of wear of the intervertebral discs.
Summary:
- Cervical spondylosis is degenerative-dystrophic changes in the vertebrae, accompanied by the formation of disc herniation.
- Cervical osteonecrosis is manifested by pain in the neck, limited movement and muscle spasms. When spinal roots are compressed by a herniation, muscle weakness and skin numbness in the upper extremities may occur.
- Diagnosis of cervical spondylosis includes examination by a neurologist and conducting the necessary additional examinations: CT, MRI of the spine and other methods.
- Treatment for osteoarthritis is typically conservative and aimed at reducing pain, inflammation, and muscle spasms.
- Prevention of osteoarthritis includes maintaining an active lifestyle, regular physical activity and ergonomics in the workplace.